No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV), also known as pure electric vehicles, has outsold plug-in hybrid electric vehicles since the start of the decade. Intuitively one would have thought that because of the high cost of battery cells at the onset of electric vehicles that Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV’s), such as the Toyota Prius, would have been the best first step to enter the market, which the company initially did until it abandoned the technology. Traditional auto manufacturers (Big Auto) in general did not take electric vehicles seriously, leaving the task to start-ups such as Tesla to develop solutions for the consumer. In the auto industry, it is easier for new entrants to enter with new technology than compete with Big Auto, churning out engines from plants which cost has already been recovered. Thus leaving Big Auto at a disadvantage as they have to invest in research and infrastructure, playing catch up with the disruption.
The big driver’s behind the performance of BEV’s has been:
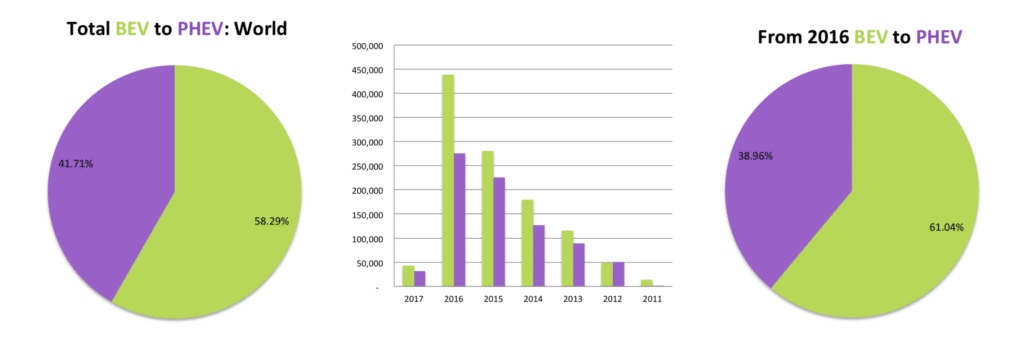
It is expected that the trend for BEV’s should remain favorable as technology and cost improvements and more automakers plan to bring BEVs to market by the end of the decade. Analyzing the Top 10 EV markets, which represent over 90% of all EVs sold, however, show the opposite. Surprisingly, at closer inspection, PHEV’s are gaining on BEV’s in the majority of the Top 10 EV markets. In our study below we compare the proportion of BEV’s to PHEV’s in the Top 10 EV markets by plotting all EV’s sold from the start of the decade to EV’s sold since 2016, when most automakers changed their electric vehicle strategies. (For more detail follow the links to the different countries for a complete breakdown of sales per model and year in that country).
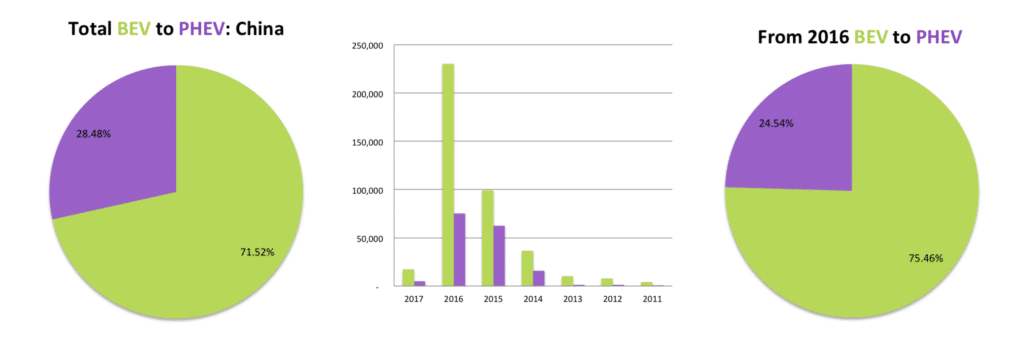
Chinese BEV’s, not always the most beautiful looking cars, have performed very well since the start of the decade and even more so over our test period from 2016. There are only three PHEV’s of any value worth mentioning in China, namely the BYD Qin, BYD Tang and SAIC Roewe 550, which combined sales accounted for around 18% of all EV’s sold since the turn of the decade. 2016 for the first time saw larger sedans taking over from the micro BEV’s, with the BYD e6, BAIC EU260, and Geely Emgrand entering the Top 4 list in the country. It is clear that with aggressive government support sales for BEV’s are ever increasing in the world’s Top market for EVs.
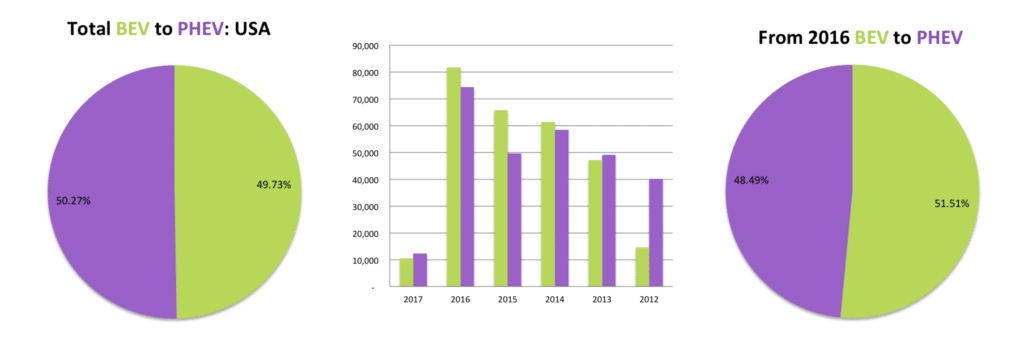
The home of Tesla and compliance vehicles, the USA, is the second largest market for electric vehicles. Stripping out Tesla, which accounts for nearly 40% of all BEV’s sold in the country will provide a completely different picture than above, where the BEV and PHEV ratio mirrors a presidential race. Most Big Auto brands are represented in the country, and when we say country, we can be forgiven to say California, where it’s Air Resource Board developed the Zero Emission Vehicle Program, targeting 15% of all vehicles to be ZEV’s by 2025. The ZEV Program supports the adoption of BEV’s by forcing automakers to sell a certain percentage of Zero Emission Vehicles. The ZEV program has been adopted by nine other states, which in total account for around 30% of all new vehicle registrations in the USA. The result is that even automakers with no EV strategy, including Fiat Chrysler, are selling what is called “compliance vehicles,” being converted plug-in variants of existing models, such as the Fiat 500e and Chrysler Pacifica. GM has also been labeled a compliance company by some, even though it introduced the first mass-market EV, the Chevrolet Bolt. The argument against GM is that it only released the Bolt it the ZEV States while it produces an uninspiring amount of 30,000 vehicles. On the other hand, GM is supporting the fight against clean air regulations and Tesla‘s direct sales model, effectively trying to halt the progress in the EV sector.
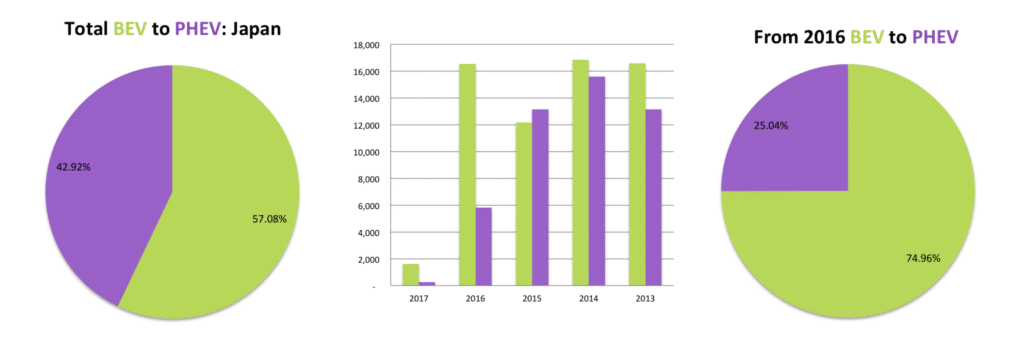
Japan, the fourth largest of the Top 10 EV markets, with China, is one of the few countries in the Top 10 list where BEV’s are outselling PHEV’s. In the case of Japan BEV’s contributed to around 75% of all EV’s sold. The country is however not the best example of expanding BEV sales. Only three brands contribute to over 90% of the sales through four models, namely the Nissan Leaf (EV), Mitsubishi Outlander (PHEV), Mitsubishi i-Miev (EV), and Toyota Prius (PHEV), which production was halted in 2015 for re-release in 2017. No great analytical deduction can be made other than a 40% increase in Nissan Leaf sales and 50% drop in Mitsubishi Outlander sales in 2016 resulted in the shift in favor of BEV’s.
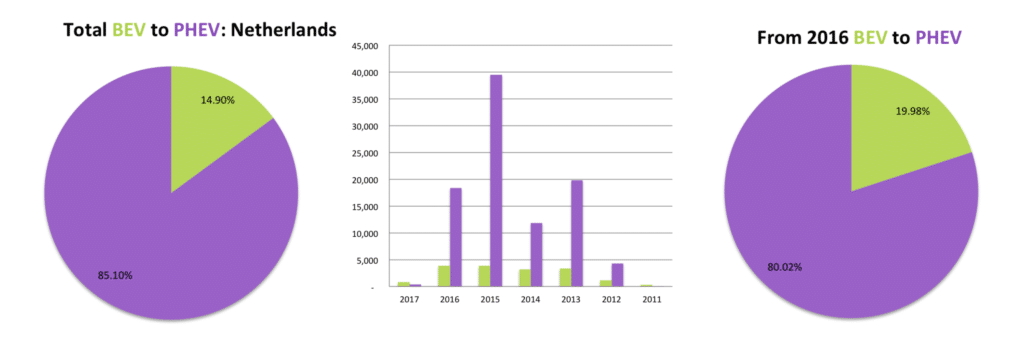 The Netherlands is a big hope for the EV sector. The country targets an 100% electric fleet by 2025. However, the data don’t really show encouragement for zero emission vehicles in a country one would have guessed would be ideal for BEV’s due to the relatively short distances within its borders ( sorry if this does not sound very Euro-centric). BEV sales have stagnated since 2013 with the Nissan Leaf and Tesla making up most of the market. The EV’s sector is dominated by PHEV’s from Volkswagen, Audi (also VW), Volvo, BMW, and Mitsubishi. The Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV is a big hit, cornering nearly 25% of the EV market in the Netherlands. The country also has the highest international sales of the Mercedes C350e, Volkswagen Passat GTE, Volvo XC90 T8 and V60 PHEV.
The Netherlands is a big hope for the EV sector. The country targets an 100% electric fleet by 2025. However, the data don’t really show encouragement for zero emission vehicles in a country one would have guessed would be ideal for BEV’s due to the relatively short distances within its borders ( sorry if this does not sound very Euro-centric). BEV sales have stagnated since 2013 with the Nissan Leaf and Tesla making up most of the market. The EV’s sector is dominated by PHEV’s from Volkswagen, Audi (also VW), Volvo, BMW, and Mitsubishi. The Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV is a big hit, cornering nearly 25% of the EV market in the Netherlands. The country also has the highest international sales of the Mercedes C350e, Volkswagen Passat GTE, Volvo XC90 T8 and V60 PHEV.
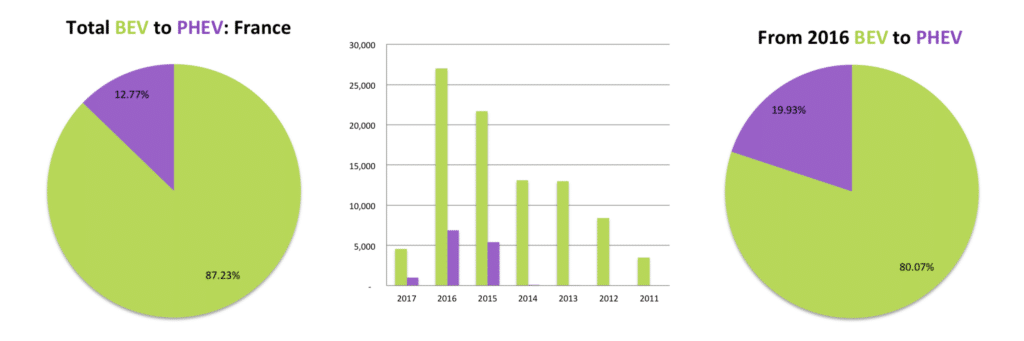 In France, the home of Renault, Citroën, Bolloré, and Peugeot is number six on the list of the Top 10 EV Markets. Here, PHEV’s have gained slightly on BEV’s but are still only 20% of all EV’s sold, while EV’s represent 1.4% of all vehicles registered in 2016. The high percentage of BEV’s is a clear indication that French automakers were more progressive in accepting electric vehicles at the turn of the decade. France also has the highest number of commercial electric vehicles, just over 15% of all EV’s, with the Renault Kangoo being the delivery vehicle of choice. France also has one of the biggest range of EV models available to the consumer, with over 50 models recorded in its official sales data.
In France, the home of Renault, Citroën, Bolloré, and Peugeot is number six on the list of the Top 10 EV Markets. Here, PHEV’s have gained slightly on BEV’s but are still only 20% of all EV’s sold, while EV’s represent 1.4% of all vehicles registered in 2016. The high percentage of BEV’s is a clear indication that French automakers were more progressive in accepting electric vehicles at the turn of the decade. France also has the highest number of commercial electric vehicles, just over 15% of all EV’s, with the Renault Kangoo being the delivery vehicle of choice. France also has one of the biggest range of EV models available to the consumer, with over 50 models recorded in its official sales data.
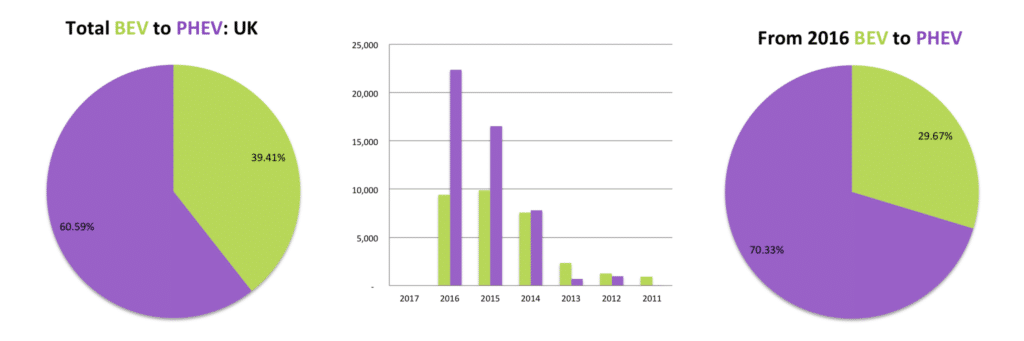
The UK market is much more excepting of PHEV’s with the trend increasing in the last year as more models are becoming available. The UK is another strong market for the Mitsubishi Outlander, where the Japanese vehicle represents nearly 30% of all EV’s sold. The world’s seventh biggest market for EV’s is also a great offset point for Germany. UK Sales for the BMW 330e is the highest in the world and sales for the Mercedes C350e is a couple of units short of the that of the Netherlands, which has the world’s most at 5,754 units. Publicly and reliable sales data for the UK is difficult to get hold of, with only the Top 5 models available up to December 2016, making a proper analysis difficult.
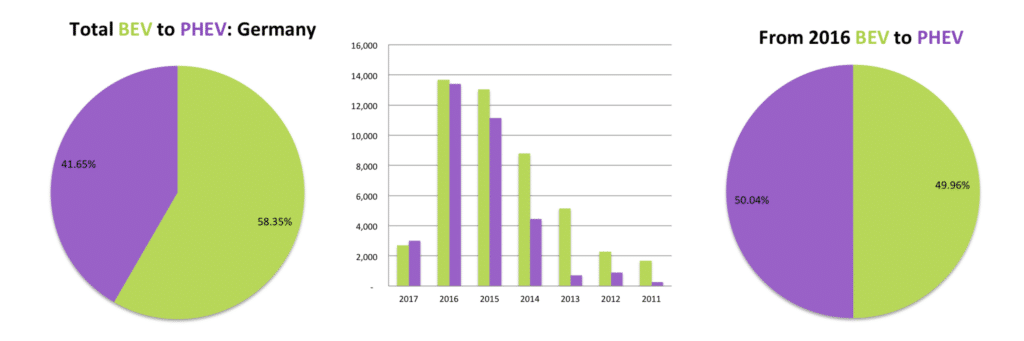
It would be surprising not to see PHEV’s beating BEV’s in the world’s 8th largest market for EV’s. Germany is home to BMW, Mercedes and VW, all brands that missed the boat on electric vehicles, now trying to catch a fast train on the back of PHEV’s. The three charts above clearly show how the release of plug-in hybrid variants of existing models since 2014 helped increase the sale of electric vehicles. Like in other European markets, the consumer is spoiled for choice in Germany.
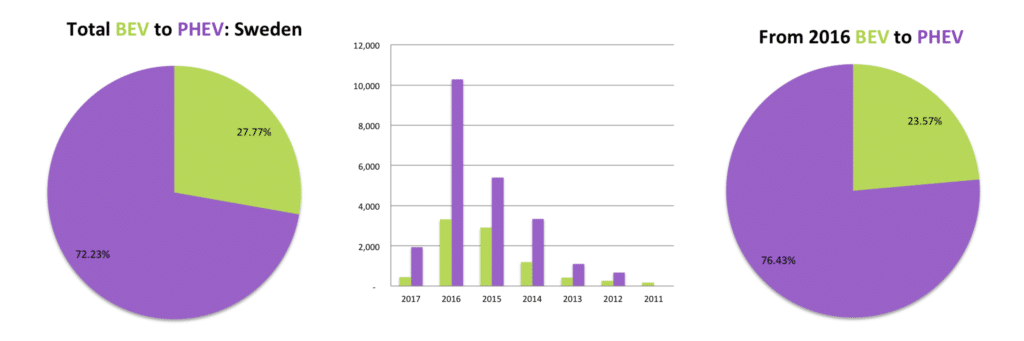
Sweden, number nine on the list of the Top 10 EV Markets and the home of Volvo also shows a big affinity for PHEV’s. The Mitsubishi Outlander again has a significant portion of the EV market, with a 25% market share of all EV’s sold. There is a significant drop between the number eight position of the Top 10 EV Markets and that of the ninth, with a 50,000 unit drop from 80,000, leaving very little to write home about. None the less Sweden commands the fourth position on the list of EV’s as a percentage of total vehicle registrations, with 3.5% of all new vehicles registered to be an EV in 2016.
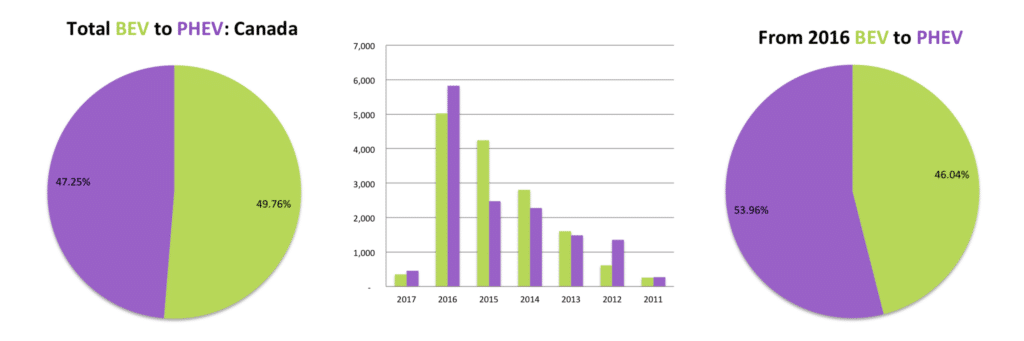
Canada in many ways mirrors the USA in trends, obviously at a much smaller scale. Just five models represent nearly 75% of all EV sales in the country, being the Chevrolet Volt, Tesla Model S, Nissan Leaf, Tesla Model X and the Smart ForTwo ED. The popularity of the Smart ForTwo makes it clear why Daimler decided to only sell electric versions of the micro car in the country.
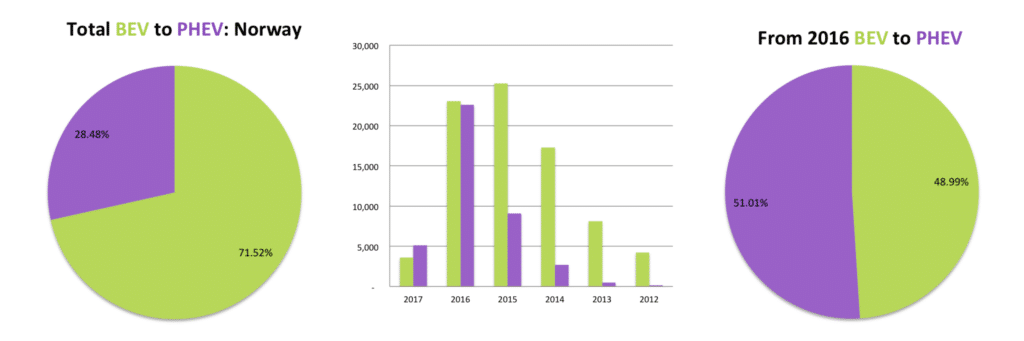
Saving the best for last. Norway, the darling of the EV sector, number three on the list of Top 10 EV markets and number one the list of EV as a percentage of new vehicle registrations. The country is now officially a growth market, reaching the take-off point for the technology, and a clear example of our thesis that PHEV’s are gaining on BEV’s. EV sales in Norway as a percentage of the total fleet for the year 2016 was at a record 29.1%. The prospects for 2017 looks even better, as in January the percentage of EV’s registered achieved a record-breaking 37.5%. At the same time, PHEV’s outsold BEV’s for the first time. Looki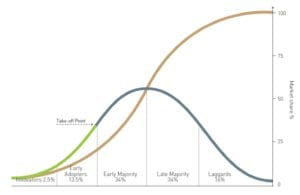 ng deeper into the data and drilling down into the model mix two things are starting to emerge, namely:
ng deeper into the data and drilling down into the model mix two things are starting to emerge, namely:
We can expect this trend to continue until there is a wider choice of BEV models for the consumer and charging infrastructure expanded. Let’s hope that this trend is not just another way for Big Auto to hijack and derail the drive to zero emission vehicles. In the meantime we should be grateful, that although not hardcore, PHEV’s still introduce new drivers to the pleasure of driving in full electric mode, thereby making them want a BEV next time they buy.
Notes on the data used for the study:
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
We have designed some cool tools to compare electric vehicles. Our tools include a mobile app, charging cost calculator and EV selector. Use wattEV2Buy’s proprietary tools to find the ideal EV for your requirements and determine the cost of charging EVs.
wattEV2Buy’s easy to use EV Select tool helps identify which electric vehicle is perfect for your specific requirements. EV Select compare electric vehicles battery electric range over various vehicle types. Within four clicks you can get the perfect luxury sedan able to drive your required distance on battery power.
wattEV2Buy’s easy to use Charging Cost Calculator compare electric vehicles charging cost in your state and relate it to equivalent gasoline cost. The charging cost calculator also allows you to be specific and customize your electricity cost in kWh and provide results in miles and kilometers, making it usable all over the world.
Top 5 EV News Week 32 2020 | Cadillac Lyriq unveiled. Yet another Chinese EV startup IPO. Three new EV models launched this week.
Top 5 EV News Week 31 2020 | Successful IPO for CHJ Auto, Kandi finally enters the USA, Mitsubishi pays the cost for failing EV strategy.
Top 5 EV News Week 30 2020 | Chengdu Auto Show, Hozon Neta IPO, VW invest in China, eVito Tourer for sale

Changing your driving style to improve the range of your Electric Vehicle and other battery management tips.
As promised in the blog “My first date with an Electric Vehicle (EV)” I will give a few pointers on efficient driving and battery management to increase range and battery life.
There is nothing more satisfying than leaving home with a range of 150 miles (240km) available, arriving at work 50 minutes later and 35km further with the available range still being the same as when you left. How is this possible you might ask? Well, it is a combination of the engineering and adapting your driving style to suit the battery system. On the engineering front, the reactive braking system charges the battery when you take your foot off the accelerator or when braking. It takes about a day to get used to this style of driving, but once you have mastered the art of anticipating the stop-start traffic you can add (or save) about 15% on the range available from your battery (figures based on my own experience). Not only do you charge your battery during reactive breaking, the engine also serves as a brake instead of you having to use the braking system. All in all the past week’s experience proved to me that an EV is the perfect vehicle for someone who spends a lot of time in traffic.
Changing one’s driving style to suit the battery system is slightly more difficult for most of us. EV’s certainly punishes aggressive driving styles, you can literarily see your battery being drained when accelerating, which is a pity. There is nothing more fun than leaving all the gas-guzzlers in your wake, especially on the pull-away at a robot. To really understand the power of an EV at a pull-away you just have to Google for YouTube clips “Tesla vs. …“ to see how a whole host of supercars struggles against an EV. My favorite is the 2016 Tesla Model X against the 2017 Bentley Bentayga. Make sure to watch the clip to the end. The BMW ConnectedDrive app certainly helps you to change your habits by informing you how efficiently you have completed each trip. My best was 82% and, dare I say it, my worst was 16%.
Here are some pointers on how changing your driving style will increase your range and improve battery life.
Although its sounds restrictive but in reality driving style has a bigger impact on a gas-guzzler from a financial perspective. Apart from the fuel cost, parts need to be serviced and replaced much more frequently than that of EV’s. In the end, it’s all just a mindset change of which you will reap the benefits of both the value of the battery and charging cost.

Contributor
Wynand studied his MBA in San Francisco where he was exposed to the fields of Service Science, Gamification, and Renewables, which he combined to create wattEV2buy and the award winning web app Ekoguru. Wynand is an energy storage expert and has modeled, designed and presented various solutions utilizing lithium-ion and other electrochemical technologies. In his spare time, Wynand is the author of a children’s book series and started a new project called “Career 180”.

I am glad to report that range anxiety is only a short-term infliction for a novice EV driver. It took only two days to overcome the fear, which I realize know is born out of ignorance or a lack of experience. I feel so confident now that I am even prepared to take up a challenge to drive the 1400km to Johannesburg, which I estimate could be done in two days.
Granted, I am driving a BMW i3 REx, which can be classified as a plug-in hybrid (PHEV), giving you that added a sense of security. Over the last four days, I have only used the combustion motor on the first day to maintain the battery’s charge level, more our of fear than necessity. In fact, the American Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) devised a measurement, called a utility factor to compare how different PHEV’s are used. The utility factor is a projection of the share of miles that will be driven using electricity by an average driver in full electric or blended modes for PHEV’s. The Toyota Prius, for instance, has a utility factor of only 29%, while the Chevy Volt has a utility factor of 66%. The BMW i3 REx has a utility factor of 83%, supporting my experience.
Naysayers will try and detract potential or novice EV drivers by stating that an emerging market like South Africa does not have the necessary infrastructure of charging stations to support the adoption of EV’s. I was shocked that the sales manager of one of the large luxury brands used this argument on me today when I tried to find out what EV’s of PHEV’s they have locally. He argued his brand only supplied the best technological solutions. Really? Not a good claim to make if the only PHEV in the parking area was that of your competitor. I sometimes wonder why people, in general, depend on the word of a sales representative to make crucial buying decisions. This manager knew nothing about EV’s but he was prepared to take a position against it and most buyers would have based their decision purely on his knowledge. I digress. Granted, we do not have the fast charging network to support long distance traveling, but as mentioned in my post on range anxiety, only a few people need to travel more than 100km’s a day, at the least making the case for an EV as a second family vehicle. I found that there is no real need for charging stations to detract you from your buying decision. During this last week, I traveled 70km a day to and from work, leaving me with ample range to travel about three days in total before re-fueling. When home I plug the vehicle into my normal wall outlet overnight to recharge the +/- 10kWh I used. In any case, there is already some charging stations planned or being constructed in South Africa. A recent article estimated that globally charging stations would be a $12.6Bln industry by 2022, which would attract entrepreneurs or large corporates to provide the service locally.
Perceived high electricity rates impacting on charging cost is another favorite counter argument for EV’s. South Africans don’t like to hear that our electricity is cheap, however, compared to international standards it is still very cheap. Currently, the average base charge per kWh in Europe of €0.22 equates to R3.74 at the current exchange rate, compared to about R2.30 in Cape Town. Charging 10kWh would cost around R23, which is far less than the estimated R80 per day I spend on fuel for the same distance. WattEV2Buy provides a great tool to measure the cost of charging and comparing the cost for the different EVs and PHEV’s.
Another favorite argument by naysayers is that an EV’s battery pack only last for a couple of years and a replacing a pack are expensive. Most EV manufacturers currently provide an 8 year / 150000km warranty of the battery pack. Eight years is a very long time in the life of any technology. Added to which, if one take into consideration the huge increase in lithium-ion manufacturing capacity over the next three years, you can expect big price decreases in the kWh price of batteries. Just in the last year lithium-ion battery, cell cost decreased from above $600/kWh to $145/kWh negotiated for the Chevrolet Bolt battery pack from LG-Chem. Furthermore, a couple of business plans already exist for the second live of EV batteries as stationary solutions for grid or battery home systems. Both Nissan and BMW have already announced efforts to create second life products, giving some value to the battery pack when it needs replacement. Internationally efforts are also afoot to utilize EV batteries as part of the smart grid, providing EV users an income from their batteries for being a demand response asset when charging or even as backup power for one’s own home. There are even some manufacturers that lease the battery, so you would only buy the “shell” of the vehicle, Citroen and Renault provide this service. Some critique to this business model is that some drivers are skeptical that the vehicle could be disabled should they miss a payment.
I can honesty say that for me, apart from price there is no real argument for not switching to an EV or PHEV at the least. Elon Musk has done humanity a big favor by bringing EV adoption forward. It forced all the large manufacturers to review their EV strategies. Up to 2014, there was still widespread skepticism on the future of EV’s. If one review the vehicle manufacturers strategies in 2016 as summarized on wattEV2buy, it is clear that most have changed course for PHEV’s and EV’s. Now the majority of big auto brands have a planned product mix of around 50% PHEV’s and EV’s by 2020.
There is only limited time left to classify yourself as an early adopter, within two years the decision to buy an EV would be mainstream and promoted by the marketing departments of all automakers.
In the next blog we look at how to get the most out of your EV’s battery and extending range.

Contributor
Wynand studied his MBA in San Francisco where he was exposed to the fields of Service Science, Gamification and Renewables, which he combined to create wattEV2buy and the award winning web app Ekoguru. Wynand is a energy storage expert and has modeled, designed and presented various solutions utilizing lithium-ion and other electrochemical technologies. In his spare time Wynand is the author of a children’s book series and started a new project called “Career 180”.